
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOD)
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOD) is a hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. It is characterized by enlarged ovaries containing small cysts, hence the name “polycystic.” PCOD disrupts the normal hormonal balance in the body, leading to a variety of symptoms and potential complications.
Causes of PCOD
There are several factors that contribute to its development, including:
Hormonal Imbalance: PCOD is associated with an imbalance in the levels of certain hormones, such as insulin, luteinizing hormone (LH), androgen, and estrogen.
Insulin Resistance: Insulin resistance, a condition where the body’s cells do not respond properly to insulin, is commonly seen in individuals with PCOD.
Genetic Predisposition: There is evidence to suggest that PCOD can run in families, indicating a genetic component to its development
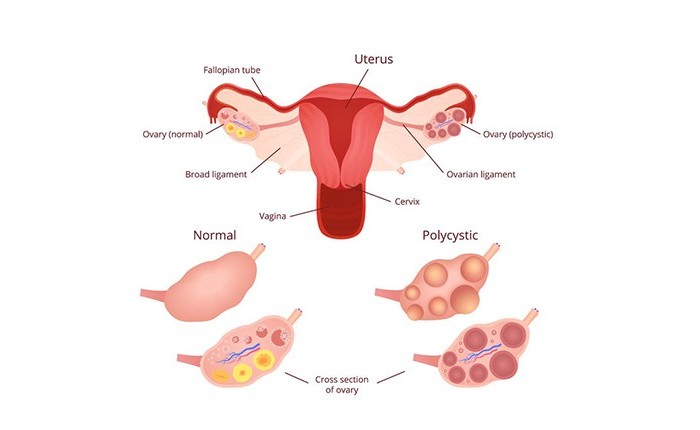

Symptoms of PCOD
PCOD presents a wide range of symptoms that can vary in severity from person to person. Some common symptoms include:
Irregular Menstrual Cycles: Women with PCOD often experience irregular periods or may have fewer than eight menstrual cycles per year.
Excess Androgen Levels: Elevated levels of androgen hormones may cause acne, excessive hair growth (hirsutism), and male pattern baldness.
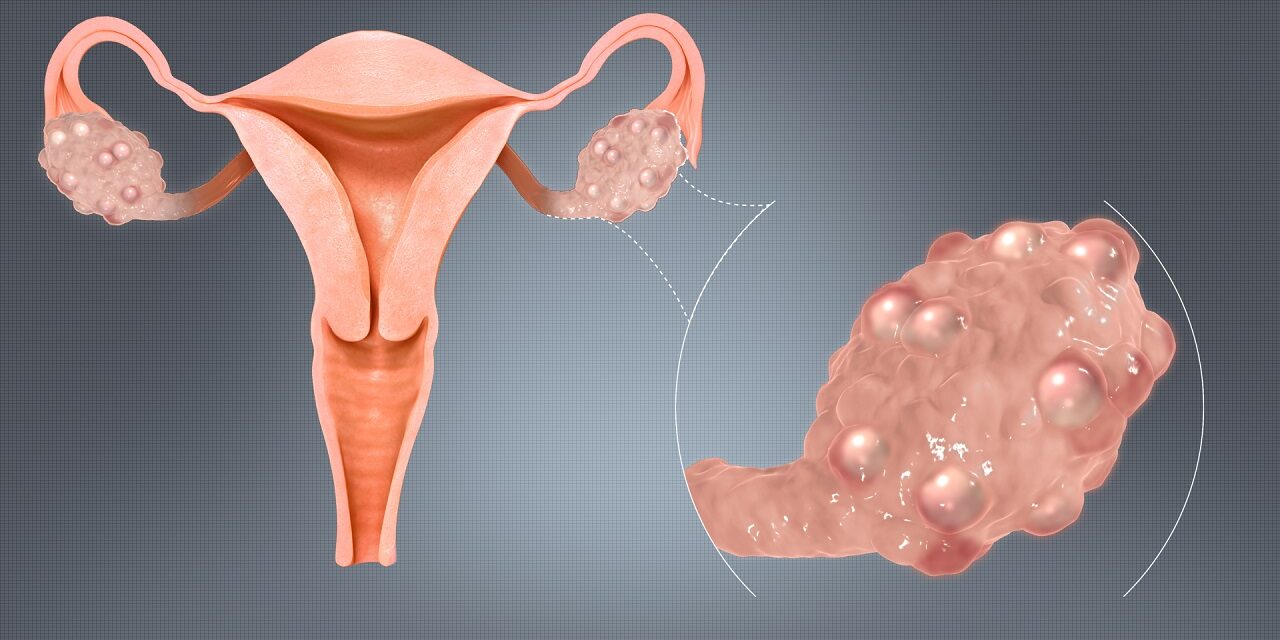
Polycystic Ovaries: Enlarged ovaries containing multiple small cysts can be detected during a pelvic ultrasound.
Weight Gain: Many women with PCOD struggle with weight gain or find it difficult to lose weight.
Infertility: PCOD can interfere with ovulation, making it challenging for women to conceive.
Skin Issues: Skin problems like oily skin, dark patches, and skin tags are commonly associated with PCOD.
Diagnosis of PCOD
Diagnosing PCOD involves a comprehensive evaluation, including:
Medical History Assessment: Your doctor will inquire about your symptoms, menstrual cycle patterns, and any relevant medical history.
Physical Examination: A physical examination may be performed to check for signs of PCOD, such as acne or excessive hair growth.
Blood Tests: Hormonal levels, including those of androgens, insulin, and other relevant hormones, will be measured through blood tests.
Ultrasound Imaging: A pelvic ultrasound may be conducted to examine the ovaries for cysts or other abnormalities.
Treatment Options for PCOD
Various treatment approaches can effectively manage the symptoms and improve overall health. Treatment options may include:
Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management can help regulate hormones and manage symptoms.
Medications: Birth control pills, anti-androgen medications, and insulin-sensitizing drugs may be prescribed to regulate menstrual cycles, reduce androgen levels, and improve insulin sensitivity.
Fertility Treatments: If fertility is a concern, ovulation induction medications or assisted reproductive technologies like in vitro fertilization (IVF) may be recommended.
Weight Management: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can help improve hormonal balance and reduce the severity of PCOD symptoms.
Surgical Intervention: In certain cases, laparoscopic ovarian drilling or ovarian cystectomy may be performed to manage specific complications of PCOD.
Schedule an Appointment
At Jogal Women’s Hospital, we understand the challenges that PCOD can bring to your life. Our experienced healthcare professionals provide comprehensive care and support throughout your PCOD journey. We offer personalized treatment plans, including medical management, lifestyle counseling, and fertility support.
Our compassionate team is dedicated to helping you manage your symptoms, improve your overall health, and achieve your reproductive goals. Please consult with our specialists to discuss your concerns, receive an accurate diagnosis, and explore the most appropriate treatment options for your individual needs. We are here to provide the care and support you deserve.

